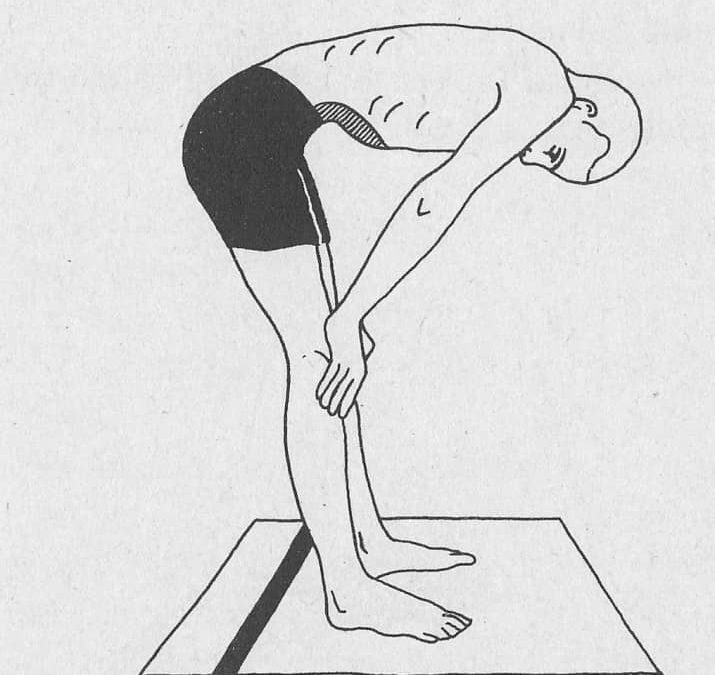
4 types of Yogic Bandha techniques
The literal meaning of Bandha is to lock, to prevent from entering, control, and close off or to stop. The special technique in yoga helps you to re-orient the energy flow to a particular area of the body where desired and prevent the energy flow to a particular area is clogged off. There are various benefits of practicing yogic bandha, the main benefit is that the energy or ‘prana’ is believed to flow inside the body. While practicing yogic bandha techniques the certain organs or parts of the body are controlled or contracted. ‘Prana’ (प्राण) means “life force”, or “vital principle” of our body.
The main work of bandhas is to flow the pranic energy through nadis (energy meridians). Likewise, other functions of bandhas include modification of the flow of nerve currents in the nervous system and smooth flow of blood through the blood vessels. Altogether, there are four main Bandhas in Pranayama, which have their own peculiarity and have their own benefits, which we will discuss in the article. The four main yogic bandha are Mula Bandha, Uddiyana Bandha and Jalandhara Bandha, and Uddiyana Bandha.
Following are the four types of bandhas
Short description:
Mula Bandha – The root lock
Uddiyana Bandha – Lifting of the Diaphragm lock
Jalandhara Bandha – The throat lock
Maha Bandha – all three locks at the same time.
1. Mula Bandha
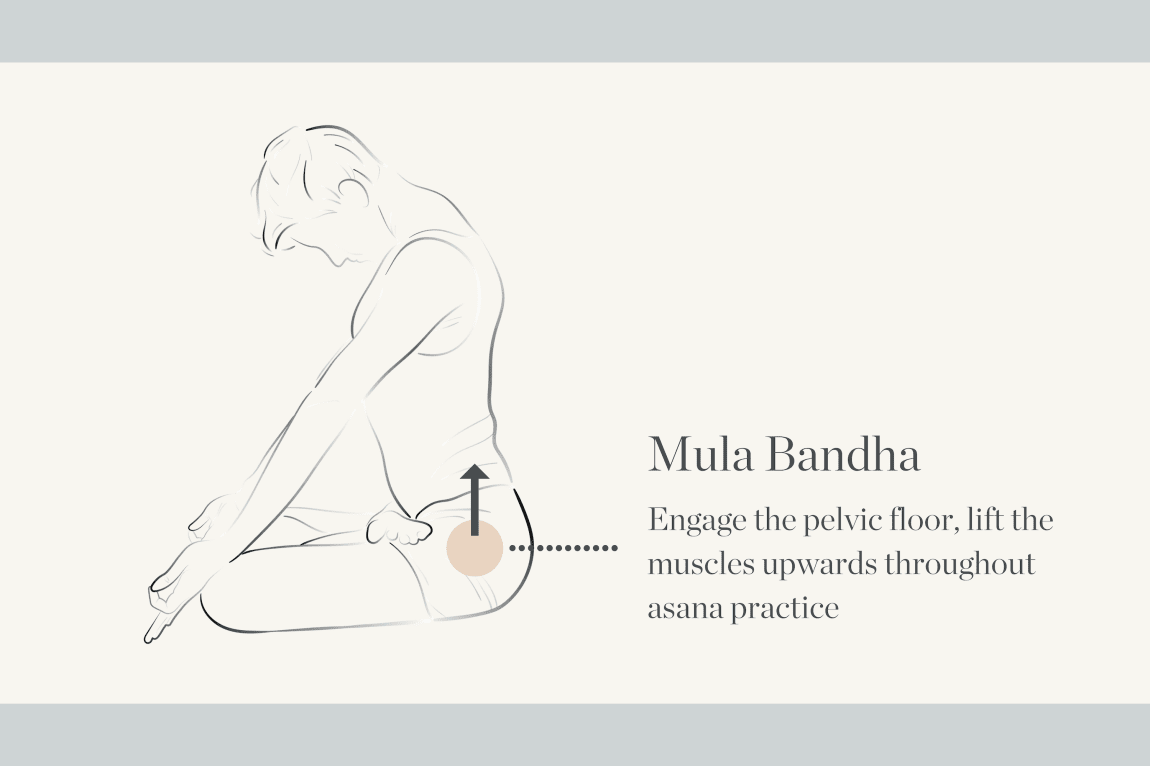
The word mula means root, or the source of origin or cause, base and the foundation. The prime location of the mula is at the base of the spine, which is also called perineum. The main function of the mula banda is to lock the energy, and halt the energy flow to downward. The clogging of the downward part prevents the flow of energy and rises the energy upward.
The asanas can be used during standing, backbends and during first chakra poses. The mula bandha asana is helpful for the organs of reproduction. The yogic bandha can be blended with PUraka (internal) or Rechaka (external) and Kumbhaka.
2. Uddiyana Bandha
The literal meaning of Uddiyana is to fly up. The technique is used for the flow of energy mainly to upward, via Sushumna Nadi. The protocol of practicing Uddiyana Bandha is to draw the abdomen in and up; likewise, the diaphragm and internal organs up into or toward the chest (thorax) is also practiced. The benefits of practicing Uddiyana Bandha are:
- Easing of the digestion process through buttressing of the digestive organs.
- Energize and strengthens the abdominal muscles.
- Helps to energize the organs of the body.
3. Jalandhara Bandha
The literal meaning of Jalandhara is a net, a web, a lattice or a mesh. The protocol of practicing Jalandhara Bandha is to contract the neck and throat. While practicing the techniques, the chin is lowered and taken towards the chest by lengthening of the neck. While there are various benefits of practicing Jalandhara Bandha, if it is practiced improperly then the pressure starts to exert on the eyes, ears and brain and causes different problems like headaches and others.
4. Maha Bandha- Includes all 3 yogic Bandha
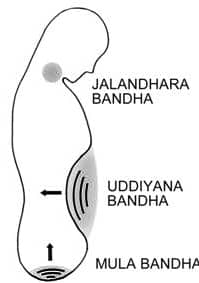
When all three bandhas: Mula Bandha, Jalandhara Bandha, Uddiyana Bandha are engaged together, the energy starts to meet together at a specific point in the navel. This practice is called Maha Bandha. The energy increases and helps to awaken various nadhis and the nadi suddhi takes place by practicing maha bandha. The main purpose of practicing bandha is to awaken and purify prana.
All in all the purpose of practicing all forms of yogic bandha is to make and buttress the ability to regulate the energy. Mainly the energy through out the body is regulated.